- Your cart is empty
- Continue shopping
Chickenpox: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & Prevention | MVD Pharmacy
Chickenpox, additionally accepted as varicella, is a awful catching viral infection that primarily affects accouchement but can additionally action in adults. Though generally advised a adolescence disease, chickenpox can advance to austere complications in assertive populations, abnormally newborns, adults, abundant women, and individuals with attenuated allowed systems.
In this blog, we’ll awning aggregate you charge to apperceive about chickenpox, including causes, symptoms, stages, analysis options, prevention, and vaccination
Table of Contents
What is Chickenpox?
Chickenpox is acquired by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV). Once addition is infected, the virus charcoal abeyant in the anatomy and can clean years later, causing shingles (herpes zoster).
It spreads through:
- Direct contact with the rash
- Coughing or sneezing of an infected person
- Touching contaminated objects or surfaces
Chickenpox is more common in children under the age of 12, but adults can contract it too, often with more severe symptoms.
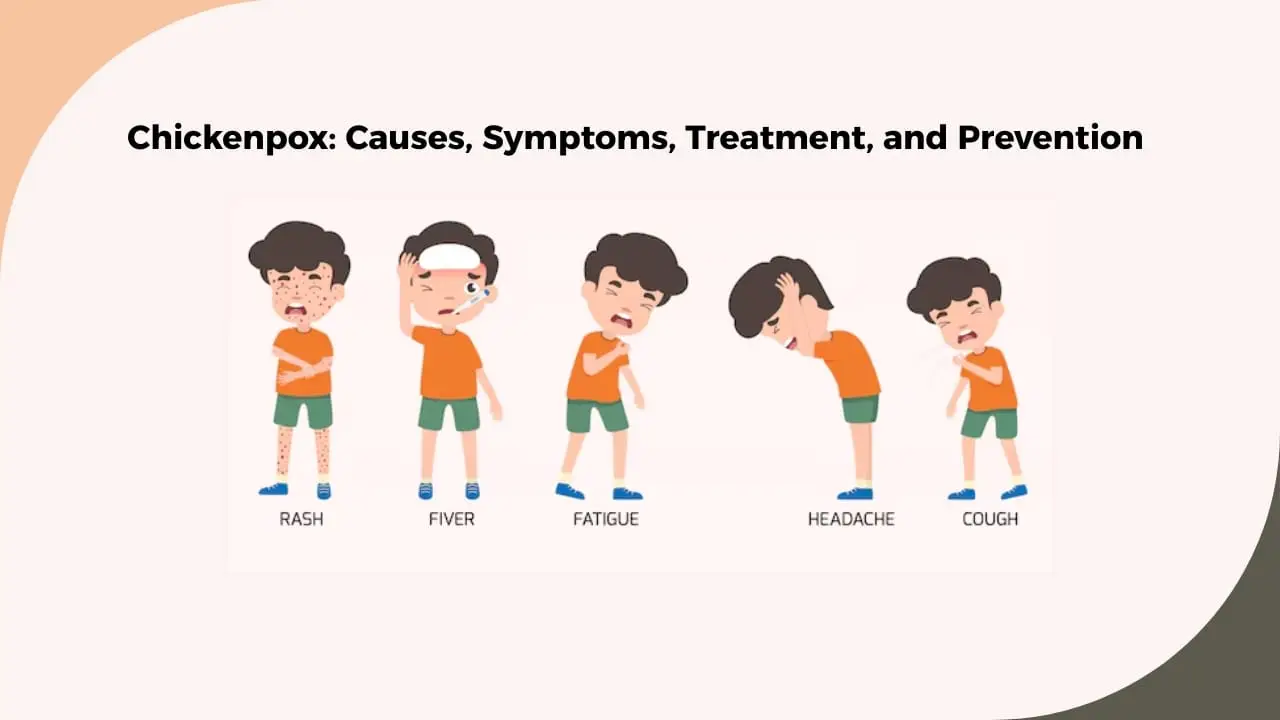
Symptoms of Chickenpox
Symptoms typically appear 10–21 days after exposure to the virus. Common symptoms include:
- Fever
- Fatigue and irritability
- Loss of appetite
- Headache
- Itchy, blister-like rash
Rash Stages:
- Red Spots: Initial appearance, flat and small
- Blisters: Filled with fluid, very itchy
- Burst and Crust: Blisters break and form crusts
The rash usually starts on the face, chest, and back, then spreads to the rest of the body, including inside the mouth, eyelids, or genital area.
Causes and Risk Factors
Risk Factors:
- Not being vaccinated
- Being under 12 years old
- Living with someone infected
- Weakened immune system
- Pregnancy (for unborn child)
Diagnosis
Doctors usually analyze chickenpox based on arresting symptoms, abnormally the rash. In attenuate cases, lab tests or claret assignment may be done to affirm the attendance of the virus.
Treatment for Chickenpox
Most cases are balmy and boldness aural 7 to 10 days. However, analysis focuses on abating symptoms:
Medications:
- Paracetamol (for fever and pain relief; avoid aspirin)
- Antihistamines (for itching)
- Antiviral Drugs (acyclovir in severe cases or at-risk patients)
Home Remedies:
- Cool oatmeal baths
- Calamine lotion
- Wearing loose, cotton clothing
- Keeping fingernails short to prevent skin infections from scratching
What to Avoid:
- Scratching the blisters
- Using aspirin (risk of Reye’s syndrome in children)
- Contact with pregnant women, infants, or immunocompromised individuals
Complications of Chickenpox
While usually mild, chickenpox can lead to complications such as:
- Bacterial skin infections
- Pneumonia
- Encephalitis (brain inflammation)
- Reye’s Syndrome (rare, associated with aspirin use)
- Shingles later in life
Chickenpox in Adults and Pregnant Women
Adults tend to have more severe symptoms. Chickenpox during pregnancy can lead to:
- Congenital varicella syndrome (birth defects)
- Miscarriage or premature delivery
Prompt medical care is essential in these cases.
Prevention of Chickenpox
1. Vaccination
The best way to prevent chickenpox is through the chickenpox vaccine (Varivax). It is:
- 90% effective in preventing chickenpox
- Usually given in 2 doses: at 12–15 months and 4–6 years
Adults who haven’t had chickenpox or the vaccine should consult their doctor about getting vaccinated.
2. Hygiene and Isolation
- Isolate infected individuals for at least 5–7 days after the rash appears
- Regular handwashing
- Disinfect surfaces
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical absorption if:
- Rash spreads to eyes or turns actual red and tender
- You or your adolescent has adversity breathing
- The agitation exceeds 102°F (38.9°C)
- You’re abundant or immunocompromised and apparent to chickenpox
Chickenpox vs. Shingles
- Chickenpox: First-time infection caused by VZV
- Shingles: Reactivation of VZV later in life
People who have had chickenpox are at risk for shingles. The shingles vaccine is recommended for people over 50.
Conclusion
Chickenpox may be common, but it’s far from harmless—especially for accessible groups. With vaccination, awareness, and able care, you can finer assure yourself and your admired ones.
Always argue a healthcare provider for alone medical advice.
Dr.Babu Rafeeq taks about Spread & Treatment of Chickenpox
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is chickenpox contagious before the rash appears?
Yes, chickenpox is contagious 1–2 days before the rash appears and remains contagious until all blisters have crusted over.
Q2. Can a person get chickenpox twice?
It’s rare, but possible. However, most people develop immunity after the first infection.
Q3. Is the chickenpox vaccine safe?
Yes, it is safe and effective. Side effects are usually mild (fever, soreness).
Q4. Can adults take the chickenpox vaccine?
Yes, adults who haven’t had chickenpox or been vaccinated should consider it.
Q5. How long does chickenpox last?
It typically lasts 7 to 10 days.
Q6. Can chickenpox be serious?
Yes, especially in adults, pregnant women, and people with weak immunity.